Security System Maintenance Checklist: 7 Key Steps
- Бонус за регистрацию онлайн казино
- Jul 15, 2025
- 14 min read
Investing in a state-of-the-art security system is a critical first step, but its true value is only realized through consistent, proactive upkeep. The assumption that technology works perfectly forever is a significant vulnerability. A dirty camera lens, a dying backup battery, or a miscalibrated sensor can render your entire system ineffective precisely when you need it most. From a construction site manager relying on mobile security trailers to a business owner managing remote access control, a lapse in maintenance can lead to catastrophic security failures and financial losses.
This is where a detailed security system maintenance checklist becomes your most powerful tool. It transforms upkeep from a reactive chore into a proactive defense strategy. This guide moves beyond simple reminders to provide a structured, actionable framework for inspecting every critical component of your security infrastructure. We will cover the specific, technical checks required for camera systems, access control points, intrusion sensors, and network integrity. Following these steps ensures your 4K security cameras capture clear evidence, your alarm systems function during a power outage, and your overall security investment continues to deliver uncompromising protection. Think of this checklist as an operational blueprint to maintain peak performance and safeguard your assets without fail.
1. Camera System Inspection and Cleaning
Your surveillance cameras are the primary eyes of your security system, making their regular inspection and cleaning a non-negotiable part of any effective security system maintenance checklist. Over time, lenses accumulate dust, grime, pollen, and water spots, which can obscure the view and render high-resolution 4K security cameras ineffective. A thorough inspection ensures each camera, from a wide-angle 360 surveillance camera to a specialized LPR camera, is functioning optimally and positioned correctly to eliminate blind spots.

Neglecting this task is like asking a security guard to watch monitors with a blindfold on. The footage becomes grainy, blurry, or completely blocked, which can be disastrous when you need to identify a suspect, read a license plate, or verify an incident at a construction site or event venue.
How to Perform a Camera Inspection and Cleaning
A comprehensive camera check involves more than just a quick wipe of the lens. It's a systematic process to guarantee peak performance and longevity, especially for assets like portable solar camera trailers exposed to harsh elements.
Your step-by-step process should include:
Visual Inspection: Check the camera housing for any signs of damage, vandalism, or corrosion. Ensure mounts are secure and haven't been tampered with. Look for insects or spiderwebs that could obstruct the lens or trigger false motion alerts.
Lens Cleaning: Use a can of compressed air to blow off loose dust and debris first. Then, apply a lens-specific cleaning solution to a clean microfiber cloth (never spray directly onto the lens) and gently wipe in a circular motion. This prevents scratches that can permanently degrade image quality.
Position and View Verification: Log into your remote camera monitoring system to confirm the camera's field of view is unobstructed. Trim any new tree branches or move new obstacles that may have appeared. Verify that the camera's position hasn't shifted due to wind, vibration, or tampering.
Housing and Seal Check: For outdoor cameras, inspect the weather seals and gaskets to ensure they are intact and preventing moisture intrusion, which can fry internal components.
Key Insight: Document your maintenance with before-and-after photos of the camera's view. This creates a visual log of your efforts and helps justify maintenance schedules to stakeholders, proving the direct impact on image clarity and security effectiveness.
2. Access Control System Testing
Your access control system is the gatekeeper of your facility, dictating who can and cannot enter sensitive areas. Regular testing of these components, from card readers and keypads to biometric scanners and electronic locks, is a critical element of any security system maintenance checklist. This systematic verification ensures that authorized personnel can enter seamlessly while maintaining robust security barriers against unauthorized access, safeguarding people, assets, and data.
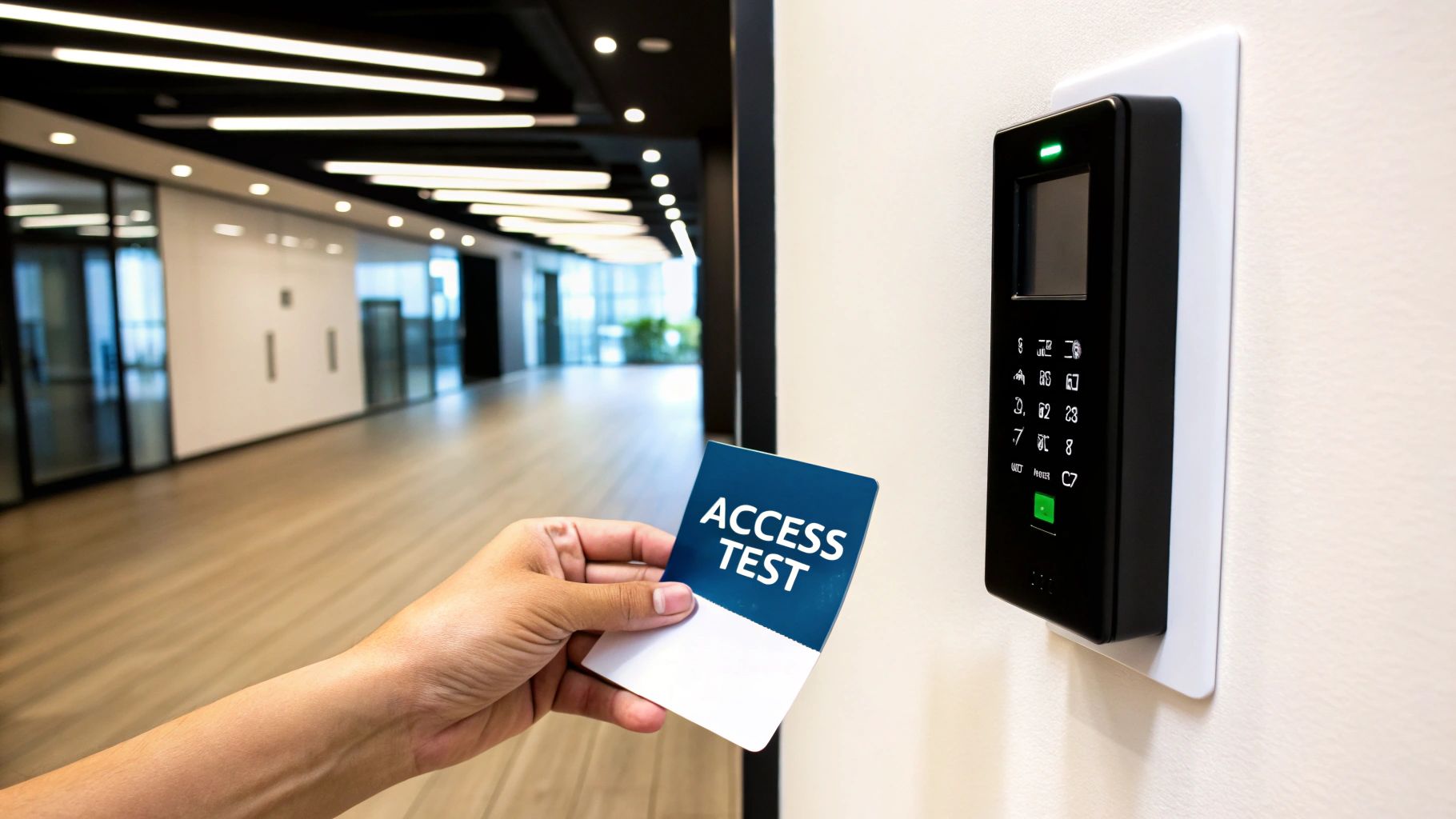

Failing to test these systems can lead to catastrophic breaches. A malfunctioning lock on a server room door could expose sensitive data, while a faulty reader at a hospital's ICU could compromise patient safety. Regular validation, such as the comprehensive quarterly audits performed at government facilities, ensures every entry point functions exactly as intended, preventing security gaps from forming over time.
How to Perform an Access Control System Test
A thorough test goes beyond simply swiping a single card. It's a methodical process designed to validate the entire access pathway, from the credential itself to the locking mechanism and the software that manages it all.
Your step-by-step process should include:
Credential and Reader Verification: Test a variety of credentials at each reader, including active employee badges, temporary passes, and, most importantly, recently deactivated credentials to ensure they are denied access. Verify that both primary and backup access methods, like PIN codes or mobile credentials, are working.
Lock and Egress Hardware Test: Physically inspect all controlled doors. Confirm that electronic locks engage securely and release promptly upon valid authentication. Test request-to-exit buttons and motion sensors to ensure they allow for safe and immediate egress, a critical life-safety function.
System Log and Alert Review: Log into your access control software and review event logs. Check for any anomalies, such as an unusual number of "access denied" events at a specific door, which could indicate a failing reader or a concerted attempt at unauthorized entry.
Access Level Audit: Regularly coordinate with HR to audit your access control list. Ensure that employee permissions are up-to-date, reflecting any recent job changes or terminations. Removing credentials for former employees promptly is a fundamental security practice.
Key Insight: Create and maintain a detailed log of all your test results, noting the date, location, credential used, and outcome (pass/fail). This documentation is invaluable for troubleshooting, demonstrating compliance during security audits, and identifying components that may require replacement before they fail completely. As you test your systems, consider strategies for enhancing access control with multi-factor authentication to bolster your security posture.
3. Intrusion Detection Sensor Calibration
Your intrusion detection sensors are the silent sentinels of your security network, designed to instantly flag unauthorized entry. However, without precise calibration, these sensors can become a source of frustration, either failing to detect real threats or, more commonly, generating a high volume of false alarms. This step in your security system maintenance checklist ensures that motion detectors, glass break sensors, and door contacts are finely tuned to your specific environment, providing reliable protection.

Improperly calibrated sensors undermine the entire system's integrity. A warehouse motion detector that triggers every time the HVAC system kicks on will lead to alarm fatigue, where legitimate alerts may be ignored. Conversely, a poorly configured glass break sensor in a jewelry store might fail to activate during a smash-and-grab, rendering a critical layer of defense useless.
How to Perform Sensor Calibration
Effective calibration goes beyond default settings, tailoring sensor sensitivity and logic to the unique conditions of its location. This process minimizes false positives while maximizing detection accuracy for everything from portable solar camera trailers to permanent building installations.
Your step-by-step process should include:
Environmental Assessment: Before touching any settings, analyze the sensor's environment. Note sources of potential interference like air vents, heaters, reflective surfaces, sources of vibration, or even pests. For example, a PIR motion detector near a south-facing window may trigger from direct sunlight.
Walk-Testing: Arm the system and physically test each sensor's detection range and sensitivity. Walk through a motion detector's coverage area at different speeds and angles. Use a specialized tester or a key jingle to simulate the frequency of breaking glass near an acoustic sensor. Open and close protected doors and windows.
Sensitivity Adjustment: Based on walk-test results, carefully adjust the sensor's sensitivity settings. Many modern sensors from brands like Bosch or Honeywell offer pulse count or sensitivity jumpers. The goal is to find the sweet spot that detects a human intruder but ignores minor environmental disturbances.
Log and Document: Record the baseline settings before you begin and document every adjustment made. This log is invaluable for future troubleshooting and helps maintain consistency, especially across multiple sites or if different technicians perform maintenance.
Key Insight: Schedule sensor calibration during off-hours to avoid disrupting business operations. Testing under the quietest possible conditions provides a clear baseline, making it easier to identify how normal daily activities might impact sensor performance and adjust accordingly.
4. Alarm System Battery Backup Testing
Your security system's resilience is only as strong as its weakest link, and during a power outage, that link is often the battery backup. A comprehensive evaluation of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup batteries is a critical component of any security system maintenance checklist. These power sources are designed to keep your alarms, cameras, and access control systems operational during electrical disruptions, ensuring continuous protection when your property is most vulnerable.
Failing to test these backups is a gamble against the unexpected. A dead battery means a power cut, whether from a storm or intentional sabotage, instantly disables your entire security infrastructure. For a bank's ATM, a hospital's critical care area, or a manufacturing facility's perimeter, this downtime creates an unacceptable security gap.
How to Perform Battery Backup Testing
A thorough battery test simulates a real-world power failure, verifying that your system can sustain itself and perform all its critical functions without interruption. This goes beyond checking a status light; it's a hands-on verification of power-readiness.
Your step-by-step process should include:
Simulated Power Outage: With proper notification to stakeholders, carefully disconnect the main power to the security panel or system. The system should seamlessly switch to its battery backup without any interruption in service. This is best performed during scheduled site maintenance.
Component Functionality Check: While on battery power, test key components. Trigger a door sensor, activate a motion detector, and access a live feed from a remote camera. Confirm that all devices remain online and responsive, ensuring the battery's output is sufficient for the entire system load.
Duration and Performance Log: Document how long the system runs on battery power and note any performance degradation. Keep a detailed log of each test, including the date, duration, and battery voltage readings before and after. This helps identify performance trends and predict replacement needs.
Battery Inspection and Replacement: Visually inspect batteries for any signs of swelling, corrosion, or leakage. Follow the manufacturer's recommended replacement schedule, typically every 3-5 years, regardless of test performance, as battery capacity diminishes over time.
Key Insight: Ensure your backup power capacity accounts for all critical security components, not just the alarm panel. High-power devices like 4K security cameras, NVRs, and network switches must be included in the load calculation to prevent the system from failing prematurely during an extended outage.
5. Network Security Infrastructure Monitoring
Your modern security system is only as reliable as the network it runs on. Continuous evaluation of network components, including firewalls, switches, and routers, is a critical part of any security system maintenance checklist, ensuring secure data transmission and uninterrupted communication between devices like IP cameras and your central monitoring station. An unmonitored or compromised network can render your entire security apparatus useless, creating vulnerabilities for cyber-attacks or system failures.
Ignoring your network's health is like leaving the back door unlocked while guarding the front. A single misconfigured firewall or an outdated switch firmware could allow an attacker to disable cameras, intercept data, or gain access to your entire business network. This is especially true for businesses like retail chains and corporate offices that rely on IP-based systems for loss prevention and asset protection.
How to Perform Network Infrastructure Monitoring
A robust network monitoring strategy goes beyond just checking if devices are online. It involves a proactive approach to identify and mitigate security risks before they can be exploited. This is essential for protecting sensitive video feeds and system data.
Your step-by-step process should include:
Network Segmentation: Isolate your security system on a separate network or Virtual LAN (VLAN) from your general business and guest Wi-Fi. This contains potential breaches and prevents a compromise in one area from affecting your critical security infrastructure.
Implement Monitoring Tools: Deploy network monitoring software from providers like Cisco or Fortinet. Configure real-time alerts for unusual traffic patterns, device failures, or unauthorized access attempts. This allows your IT team to respond instantly to threats.
Firmware and Patch Management: Regularly check for and apply security patches and firmware updates for all network devices, including routers, switches, and wireless access points. Manufacturers frequently release updates to fix newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Conduct Penetration Testing: Periodically hire a third party to perform penetration testing on your security network. This simulated attack will identify real-world weaknesses in your firewalls and device configurations that automated scans might miss.
Key Insight: In addition to monitoring your network for digital threats, employing advanced Technical Surveillance Countermeasures (TSCM) is crucial to protect your physical and electronic environments from sophisticated eavesdropping and surveillance. A holistic security strategy defends against both digital and physical intrusions.
6. Control Panel System Diagnostics
The control panel is the brain of your entire security apparatus, coordinating every sensor, camera, and access point. A comprehensive diagnostics check is a critical part of any security system maintenance checklist, ensuring this central hub is communicating effectively and processing information correctly. Without a healthy control panel, even the most advanced 4K security cameras or access systems become isolated, unreliable components.
Ignoring control panel health is like having a skilled command team that can't communicate with its field agents. Signals are missed, alarms fail to trigger, and the entire system's integrity is compromised. This is especially true for complex sites like manufacturing plants or healthcare facilities, where the panel integrates access control, surveillance, and alarm systems into one cohesive network.
How to Perform Control Panel Diagnostics
A thorough diagnostic isn't just about seeing a "system okay" light. It's a deep dive into the panel's operational health, verifying its software, hardware, and communication pathways are all performing to manufacturer specifications. This proactive check prevents small glitches from escalating into major security failures.
Your step-by-step process should include:
System Health Check: Access the panel's diagnostic menu, a feature common in systems from manufacturers like Honeywell or Bosch. Run the built-in system health tests, which check for processor faults, memory errors, and power supply irregularities.
Communication Pathway Test: Manually trigger a test signal to your central monitoring station. Confirm they receive the signal correctly and that the panel’s primary and backup communication lines (e.g., internet and cellular) are both functional. This verifies your link for emergency response.
Configuration Verification: Review the system's configuration logs. Ensure that all connected devices, from a new LPR camera to a recently added door sensor, are correctly registered and communicating with the panel. Confirm that user access codes and permissions are up-to-date.
Event Log Review: Scan the panel's event log for unusual patterns, such as frequent communication dropouts from a specific sensor or repeated tamper alerts. These can indicate a failing device or a physical issue that needs attention before it causes a complete failure.
Key Insight: Establish baseline performance metrics during installation, such as signal strength and processor load. During each diagnostic, compare current readings to this baseline. This data-driven approach allows you to spot gradual performance degradation long before it triggers a system fault, enabling proactive repairs.
7. Emergency Response System Verification
An emergency response system is the critical link between detecting a threat and neutralizing it. This part of your security system maintenance checklist ensures that when a panic button is pushed or an automated alarm is triggered, the response is swift, accurate, and effective. Regular verification confirms that panic buttons, silent alarms, and automated communication protocols are not just installed but fully operational, ensuring a rapid response during a crisis.
Ignoring this step means your most critical safety features could fail when you need them most. Imagine a silent bank alarm that never reaches the police department or a school's lockdown system that doesn't activate. The consequences are severe, making this verification a top-tier priority for any business, construction site, or event venue.
How to Perform Emergency Response System Verification
A proper verification goes beyond just pressing a button; it involves end-to-end testing of the entire response chain, from the initial trigger to the final communication and action. This ensures every component works in concert.
Your step-by-step process should include:
Pre-Test Coordination: Always notify your central monitoring station and all relevant internal personnel before conducting a test. This prevents false alarms, unnecessary panic, and the dispatch of emergency services. Provide the specific times and locations of the planned tests.
Physical Device Testing: Manually activate each emergency device, such as fixed panic buttons under desks, wireless pendants, and duress code entries on keypads. Confirm that the system correctly registers the activation signal.
Signal Transmission Verification: Work with your monitoring service to confirm they received the alarm signal instantly. Verify that they received the correct information, including the specific zone or device that was triggered. This is vital for guiding first responders.
Automated Protocol Review: If your system has automated responses, such as locking all doors or sending mass text notifications, run a test to ensure these protocols execute without error. For example, a school might conduct a monthly test to confirm panic buttons trigger an immediate campus-wide lockdown.
Key Insight: Document the entire process, especially the response times. Record the time from button press to monitoring station confirmation and from confirmation to personnel notification. This data is invaluable for identifying bottlenecks and refining your emergency procedures for maximum efficiency.
7-Point Security System Maintenance Comparison
Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Camera System Inspection and Cleaning | Moderate: physical access and cleaning needed | Microfiber cloths, cleaning solutions, ladders | Clear video, maintained coverage, reduced damage | Banks, retail stores, corporate parking | Maintains image quality, prevents costly repairs |
Access Control System Testing | High: involves multiple device types | Technical knowledge, testing tools, coordination | Reliable access, security compliance, breach prevention | Hospitals, data centers, government facilities | Prevents breaches, ensures audit accuracy |
Intrusion Detection Sensor Calibration | High: requires technical calibration expertise | Calibration tools, environmental testing | Reduced false alarms, optimized sensor accuracy | Art galleries, warehouses, jewelry stores | Reliable threat detection, compliance adherence |
Alarm System Battery Backup Testing | Moderate: battery testing, possible downtime | Battery testers, multimeter, replacement parts | Continuous power, prevented outages, early warnings | Banks, hospitals, manufacturing facilities | Ensures system uptime, warns of battery degradation |
Network Security Infrastructure Monitoring | Very High: ongoing cybersecurity management | Specialized cybersecurity tools, expertise | Prevented cyberattacks, secure communication | Corporations, retail chains, educational institutes | Protects network integrity, detects threats early |
Control Panel System Diagnostics | High: technical diagnostics and system checks | Diagnostic tools, technical staff | System health visibility, rapid issue resolution | Airports, manufacturing plants, healthcare | Centralized system oversight, coordinated security |
Emergency Response System Verification | Moderate: coordination-intensive testing | Communication testers, timing devices | Rapid emergency response, regulatory compliance | Schools, banks, office buildings | Ensures emergency preparedness, validates integrations |
From Checklist to Confidence: Partnering for Proactive Security
Navigating this comprehensive security system maintenance checklist is more than just a procedural task; it represents a fundamental shift from a passive to a proactive security posture. Each item, from cleaning 4K security camera lenses to testing alarm battery backups, is a vital component in a larger ecosystem of protection. By consistently addressing these points, you are not just maintaining equipment, you are actively reinforcing the reliability and effectiveness of your entire security infrastructure. This diligence transforms a collection of hardware into a resilient shield that protects your assets, personnel, and operations around the clock.
Bridging Maintenance and Mastery
The true value of this checklist lies in its ability to build institutional knowledge and operational discipline. Regular maintenance uncovers vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, ensuring that every sensor, camera, and access point functions as intended during a critical event. Whether you are managing a construction site with portable solar camera trailers or securing a corporate office with advanced access control, this consistent oversight is non-negotiable. It is the difference between a system that merely exists and one that actively performs.
To effectively manage these recurring tasks, leveraging organizational tools is crucial. Utilizing resources like free Google Docs checklist templates can provide a structured framework, helping you move from a simple list to assured system reliability. This systematic approach ensures no detail is overlooked and creates a verifiable record of your commitment to security.
Partnering for Unwavering Protection
While this guide empowers you to take control of your system’s health, the complexity and time commitment can be substantial. For many business owners, event organizers, and site managers, partnering with a dedicated security specialist is the most efficient path to achieving total peace of mind. A professional service provider doesn't just follow a checklist; they bring a wealth of experience, specialized tools, and an understanding of how each component interacts.
This expert oversight ensures that subtle issues, like network latency affecting remote camera feeds or minor calibration drifts in LPR cameras, are identified and resolved before they escalate. It guarantees that your system is not just operational but optimized for your specific environment, from a 360-surveillance camera at a festival to an integrated system at a multi-tenant facility. Ultimately, mastering your security means knowing when to delegate. By entrusting your maintenance to experts, you free up your resources to focus on your core business, confident that your protection is in the most capable hands.
Don't let maintenance become an afterthought. Partner with PCI Audio-Video Security Solutions to transform your security system maintenance checklist into a fully managed, proactive protection strategy. Contact us today to ensure your security infrastructure delivers unwavering performance and complete peace of mind.







Comments